Cultural Astronomy & Navigation
"The firmament is filled with stars and planets who were once on earth, human lovers fated to chase each other
across the evening sky into eternity. Such roles are not fixed, either; the sun, moon, and morning star seem free
to take human form and roam the earth, seeking love and other adventures." - from American Indian Myths and Legends by Richard Erdoes, Alfonso Ortiz
across the evening sky into eternity. Such roles are not fixed, either; the sun, moon, and morning star seem free
to take human form and roam the earth, seeking love and other adventures." - from American Indian Myths and Legends by Richard Erdoes, Alfonso Ortiz
Cultural Astronomy
Cultural astronomy or ethnoastronomy is concerned with learning and understanding the astronomical knowledge developed by different cultures and how this knowledge impacts the daily lives of traditional groups.
vernal (adj.) - describes something that occurs in springtime or is related to springtime.
the time or date (twice each year) at which the sun crosses the celestial equator, when day and night are of approximately equal length (about September 22 and March 20).
Celestial Equator - the projection into space of the earth's equator; an imaginary circle equidistant from the celestial poles.
the time or date (twice each year) at which the sun crosses the celestial equator, when day and night are of approximately equal length (about September 22 and March 20).
Celestial Equator - the projection into space of the earth's equator; an imaginary circle equidistant from the celestial poles.
What is meant by geographic north?
noun. the direction from any point along a meridian towards the North Pole. Also called: geographic north.
noun. the direction from any point along a meridian towards the North Pole. Also called: geographic north.
The north magnetic pole is near, but not the same as, the earth's true north pole, or axis of spin. The magnetic pole wanders somewhat over many years, and is located in far northern Canada.
The angular difference between true north and magnetic north is known as the declination and is marked in degrees on your map.
How do I correct my compass to the true bearing?You can compute the true bearing from a magnetic bearing by adding the magnetic declination to the magnetic bearing. This works as long as you follow the convention that degrees west are negative (i.e. a magnetic declination of 10-degrees west is -10 and bearing of 45-degrees west is -45). Some example case illustrations are provided for an east magnetic declination and a west magnetic declination.
n nautical navigation the absolute bearing is the clockwise angle between north and an object observed from the vessel.
If the north used as reference is the true geographical north then the bearing is a true bearing whereas if the reference used is magnetic north then the bearing is a magnetic bearing. An absolute bearing is measured with a bearing compass.
The measurement of absolute bearings of fixed landmarks and other navigation aids is useful for the navigator because this information can be used on the nautical chart together with simple geometrical techniques to aid in determining the position of the vessel.
A grid bearing (also known as grid azimuth) is measured in relation to the fixed horizontal reference plane of grid north, that is, using the direction northwards along the grid lines of the map projection as a reference point.
If the north used as reference is the true geographical north then the bearing is a true bearing whereas if the reference used is magnetic north then the bearing is a magnetic bearing. An absolute bearing is measured with a bearing compass.
The measurement of absolute bearings of fixed landmarks and other navigation aids is useful for the navigator because this information can be used on the nautical chart together with simple geometrical techniques to aid in determining the position of the vessel.
A grid bearing (also known as grid azimuth) is measured in relation to the fixed horizontal reference plane of grid north, that is, using the direction northwards along the grid lines of the map projection as a reference point.
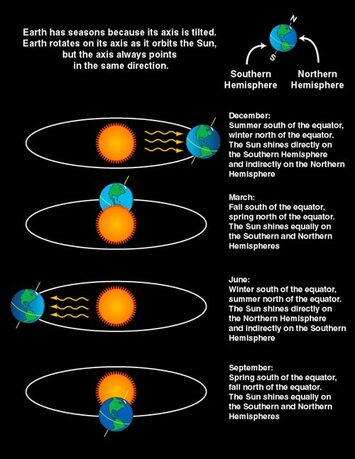
The earth's spin axis is tilted with respect to its orbital plane. This is what causes the seasons. When the earth's axis points towards the sun, it is summer for that hemisphere. When the earth's axis points away, winter can be expected.
Navigation
Cheyenne WY 41.1400° N, 104.8202° W





